Setting up nix-darwin machine for community builders
This post describes how to set up a nix-darwin machine to use community builders for Nix upstream development.
It took me a while to figure out how to set up a nix-darwin machine to use community builders for Nix upstream development. This post is a summary of the steps to get it working transparently to the user.
Assumptions
nixis configured as multi-user.- The machine is managed using
nix-darwin. - You have access to the Nix project community builders.
0: Register known host keys for community builders
This setting avoids an interactive prompt when connecting to the community builders for the first time from any user, including root.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
programs.ssh = {
knownHosts = {
"aarch64-build-box.nix-community.org" = {
publicKey = "ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIG9uyfhyli+BRtk64y+niqtb+sKquRGGZ87f4YRc8EE1";
};
"build-box.nix-community.org" = {
publicKey = "ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIElIQ54qAy7Dh63rBudYKdbzJHrrbrrMXLYl7Pkmk88H";
};
"darwin-build-box.nix-community.org" = {
publicKey = "ssh-ed25519 AAAAC3NzaC1lZDI1NTE5AAAAIKMHhlcn7fUpUuiOFeIhDqBzBNFsbNqq+NpzuGX3e6zv";
};
};
};
NOTE: Make sure keys correspond to latest keys as documented in the official docs.
1: Register Host aliases for community builders
This setting instructs all ssh clients to use a particular SSH key and username when accessing the community builders via the aliases.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
programs.ssh = {
extraConfig = let
identityFile = "/Users/${username}/.ssh/id_ed25519";
user = "booxter";
in ''
Host darwin-builder
Hostname darwin-build-box.nix-community.org
IdentityFile ${identityFile}
User ${user}
Host linux-builder
Hostname aarch64-build-box.nix-community.org
IdentityFile ${identityFile}
User ${user}
Host linux-x86-builder
Hostname build-box.nix-community.org
IdentityFile ${identityFile}
User ${user}
'';
};
This setting is important so that nix-daemon knows how to connect to the community builders.
2: Install nixpkgs SSH client as system package
This setting may be important because some SSH clients, specifically the one from Homebrew, don’t read configuration files from the /etc/ssh/ssh_config.d directory. The setting guarantees that the root user that runs the nix-daemon service will have access to Host aliases and known_hosts entries.
1
environment.systemPackages = [ pkgs.openssh ];
At this point, any user on the machine, including the root user, should be able to ssh into the community builders using the aliases defined in the previous step.
3: Use community builders with nixpkgs-review for upstream development
Since community builders are shared and not meant to be used for private builds, I do not use them for my own builds. Instead, I use them for upstream nixpkgs development to speed up my builds across multiple machines and platforms.
Instead, whenever I need to test builds with nixpkgs-review, I pass builders, with their relative preferences, to the command, as follows:
1
2
3
nixpkgs-review pr <PR_NUM> \
--no-shell --post-result --systems=all \
--build-args="--builders 'ssh-ng://rosetta-builder aarch64-linux,x86_64-linux - 2 10 - ; ssh://linux-builder aarch64-linux - 10 20 benchmark,big-parallel,kvm,nixos-test ; ssh://linux-x86-builder x86_64-linux - 5 20 benchmark,big-parallel,kvm,nixos-test; ssh://darwin-builder x86_64-darwin,aarch64-darwin - 3 20 big-parallel'"
The command will start validation of the <PR_NUM> pull request:
- for all supported platforms (
--systems=all):x86_64-linux,aarch64-linux,x86_64-darwin, andaarch64-darwin. - using the three community builders (
ssh://linux-builder,ssh://linux-x86-builder, andssh://darwin-builder). - also using the local
rosetta-builderforx86_64-linuxandaarch64-linuxplatforms (with a lower priority than Linux community builders). - tests and packages that require nested virtualization will not run on
rosetta-builder(nokvm,nixos-test). (The local daemon probably will run tests though!)- packages that require enormous resources will not be scheduled to
rosetta-builder(nobig-parallellabel).
The tool will also use the local nix-daemon for native Darwin builds. If this is not desired, you can also add --max-jobs 0 to the command.
Bonus: Monitor community builders load
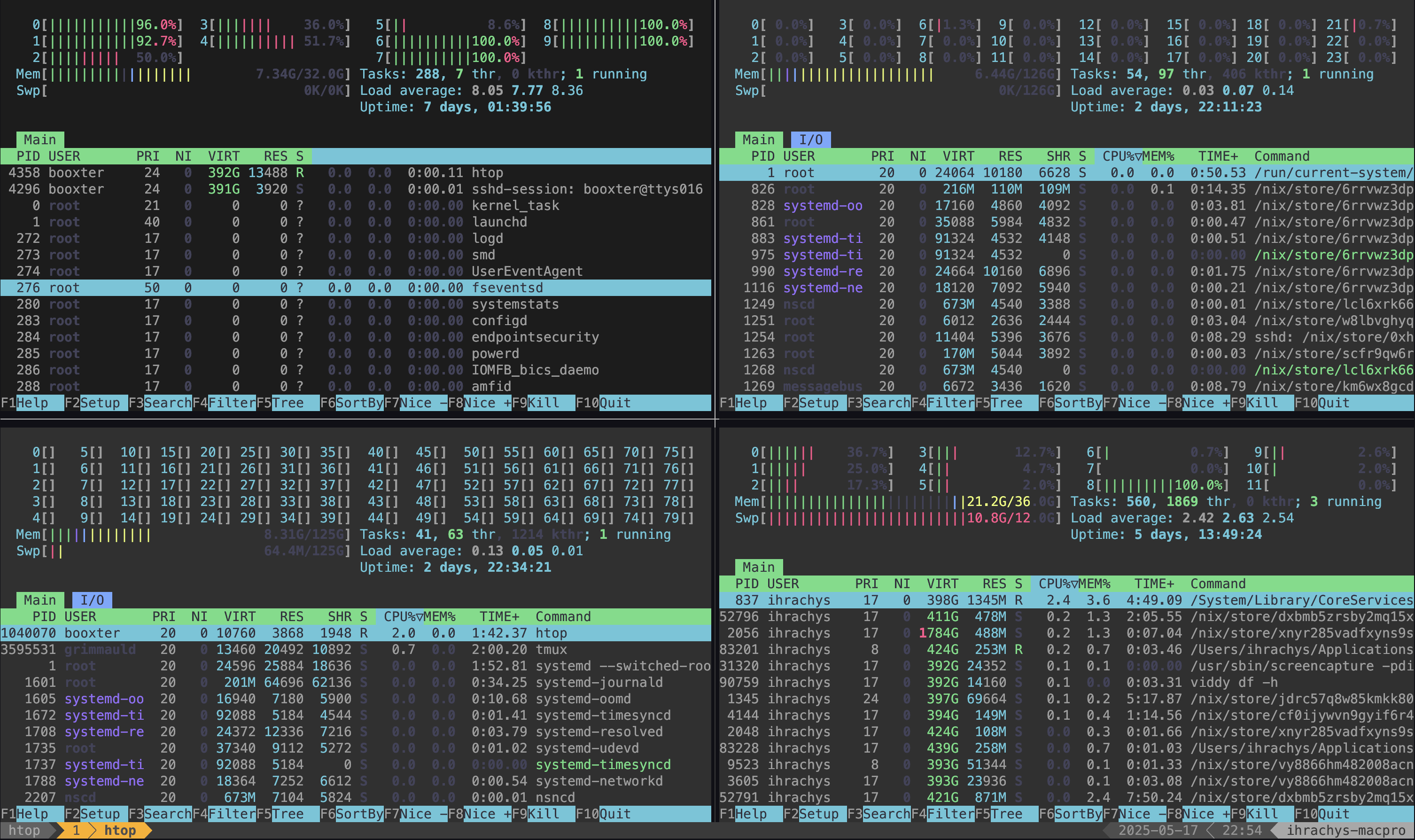
Since community builders are shared, and since nix-daemon doesn’t implement a proper job queue, it’s important to monitor the load on the community builders that your distributed builds produce.
This script will run a tmux session with four panes, each running htop for a build machine: three for community builders plus one for the local daemon.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
#!/usr/bin/env bash
HOSTS=(
"darwin-builder"
"linux-builder"
"linux-x86-builder"
"localhost"
)
# Check if tmux is installed
if ! command -v tmux &> /dev/null
then
echo "tmux could not be found. Please install it first."
exit
fi
# Check if a tmux session is already running
#
if tmux list-sessions 2>/dev/null | grep -q "htop"; then
echo "A tmux session named 'htop' is already running. Attaching to it..."
tmux attach-session -t htop
exit 0
fi
# Create a new tmux session
tmux new-session -d -s htop
# Split the window into 4 panes
tmux split-window -h
tmux split-window -v
tmux select-pane -t 1 # I start my panes numbers from 1, not 0
tmux split-window -v
# Send htop command to each pane
for i in "${!HOSTS[@]}"; do
host="${HOSTS[$i]}"
tmux select-pane -t $((i+1))
if [[ $host == "localhost" ]]; then
tmux send-keys "htop; exit" C-m
else
tmux send-keys "ssh -t $host 'htop'; exit" C-m
fi
done
# Select the first pane
tmux select-pane -t 0
# Set the window name
tmux rename-window "htop"
# Attach to the tmux session
tmux attach-session -t htop
Community builders are often restarted to apply updates, at which point the corresponding pane is closed. I’m sure there is a way to automatically reconnect but I went with a binding to kill the tmux window:
1
bind-key -T prefix K confirm-before -p "Kill session #S? (y/n)" kill-session